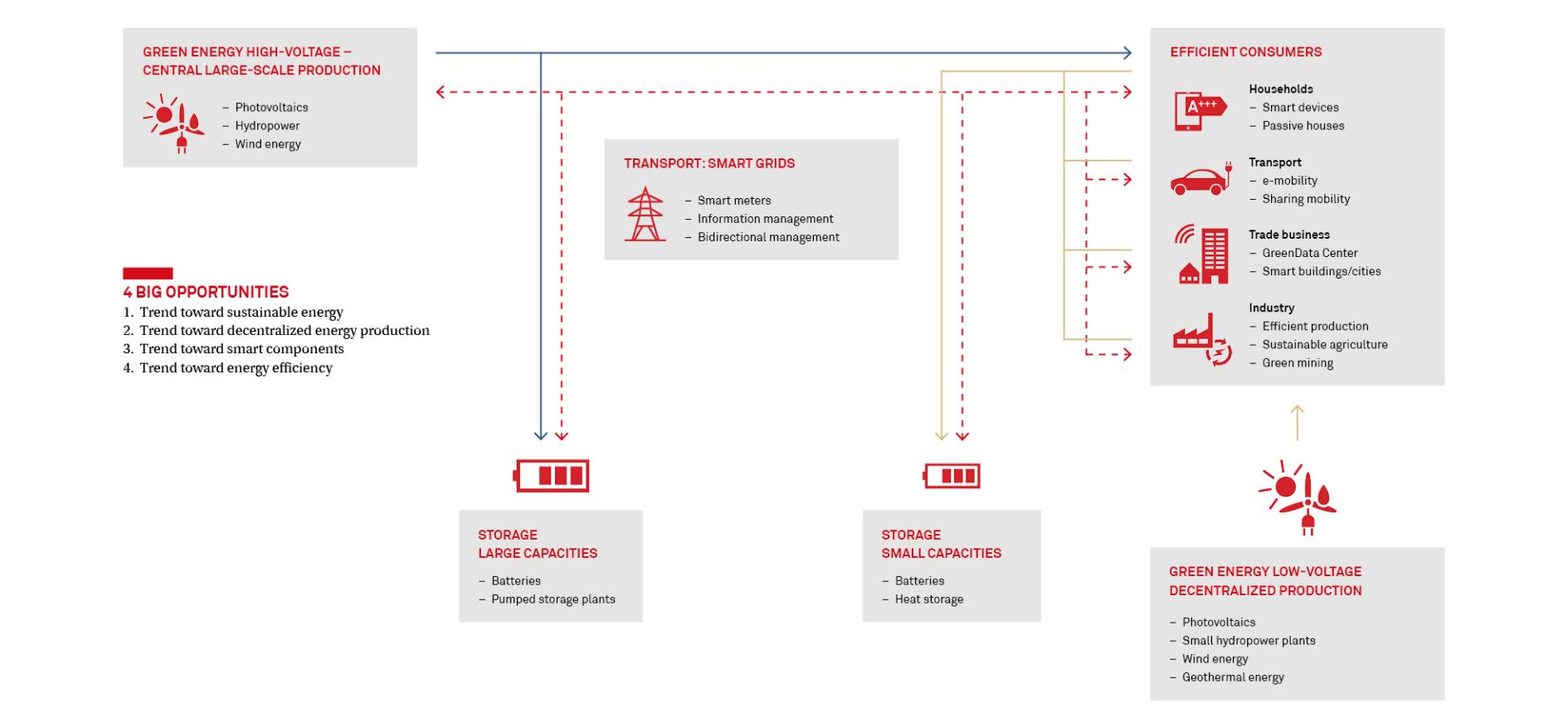
Even today, immense investments are being made worldwide in restructuring the economy and society to achieve the ambitious sustainability goals of the United Nations, with green energy playing a dominant role in the media coverage. Swiss SMEs that only think about large-scale government investments in renewable energy production capacities – the classic market for large, internationally oriented corporations – may be missing out on important trends and market opportunities.
Trend toward sustainable energy: Buffer capacities and grid development
Large power plants and especially nuclear power plants generally produce a more constant amount of energy. Simple high and low tariff models and correspondingly statically controlled consumerssuch as electric storage units are designed to avoid fluctuations in demand and thus grid loads compared to constant production volumes. However, with the ever-increasing share of renewable energy such as wind and solar, the amount of energyproduced also fluctuates, making it necessary to have compensation mechanisms such as large electricity storage facilities or power plants that can be quickly switched on using conventional energy sources. Larger and smaller battery storage systems for stabilizing electricity grids not only earn money by releasing electricity into the grid but also get paid for absorbing excess production.
In the future, more stable grids and buffer storage will be an indispensable part of the energy infrastructure and already offer market opportunities for suppliers who can plan, build, control, and equip such plants.
Trend toward decentralized energy production Bidirectional flow of electricity, networking and smart meters
The self-production of sustainable energy by commercial and private users with photovoltaic, geothermal and small hydropower plants is in itself creating rapidly growing markets worldwide. In Australia alone, more than 2.6 million private individuals are already producing electricity from solar energy thereby presenting grid operators with completely new challenges. This is because conventional concepts for energy supply are based on centralized production in large power plants that feed their largely constant output into high-voltage grids that transport the electricity over long distances to the vicinity of consumers. There, it is transformed into medium and low voltage – also with losses – and consumed locally. The flow of electricity is by and large provided in one direction only. With the ever-increasing number of local electricity production systems such as photovoltaics or small run-of-river power plants, consumers only use the electricity from the grid in a complementary manner or even feed additional energy into the grid locally. Many electricity grids have not yet been flexible enough to allow electricity to flow flexibly between local producers and to bill them transparently. Industrial parks, housing estates, commercial centers, cooperatives as well as smaller communities offer potential here for innovative providers of such solutions that are independent of energy companies.
Trend toward smart components: Increasing demand on information management
Modern components of a new, sustainable energy infrastructure all offer intelligent functions in their own way: Smart devices can draw energy when it is readily available and cheap, smart buildings and passive houses manage their energy needs internally as they move toward self-sufficiency or even overproduction. However, the real hurdle is often still the way in which information is managed among the components, and thus the optimization of the entire system. In the future, smart grids will be able to increase the overall efficiency of the energy supply by orders of magnitude compared to today through precise predictions of the production volume in combination with the management of buffer capacities and smart consumers.
This requires innovative solution providers worldwide in the area of software and hardware. From sensors to data transport and control components to the classic electricity infrastructure, there is an enormous need for investment here, and this creates opportunities for suppliers who can offer these components.
Trend toward energy efficiency: Conversion and replacement of existing infrastructure
Most existing industries play a major role in economies around the globe and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future. Even industries that are problematic from a sustainability point of view, such as mining, are investing large amounts in the energy-efficient conversion of their processes. For example, the Chilean copper industry is in the process of converting its mining vehicles to electric drive and converting its air conditioning and ventilation systems to be more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient. Government programs and regulations, such as those in Indonesia, are imposing short- and medium-term energy savings of up to 30 percent on entire industries. These mandatory requirements also create high short-term demand for know-how and suitable niche products, which offer opportunities for Swiss companies.